
Now it is a fact that the nuclear charge is SHIELDED very poorly by incomplete electronic shells. The chemistry and atomic structure of the elements is a contest between (i) nuclear charge, conveniently represented by #Z_"the atomic number"#, and (ii) shielding by other electrons. Group Theory suggests that only ions in high-symmetric non-polar crystal lattices can accurately be measured for their radii.#"Increase in atomic radii down a Group, a column of the Periodic"#"Table."# For the same ion, the radii can differ in different crystal lattices due certain variables such as coordination number and electron spin.

Ionic radii are not fixed properties of ions.With this reference point, Pauling was able to calculate the ionic radii of other ions. After studying many compounds, Linus Pauling found that the approximate ionic radii of O 2- was 140pm. Ionic radii are measured by proportioning ionic bond lengths between two ions within a crystal lattice.Zr 4 +
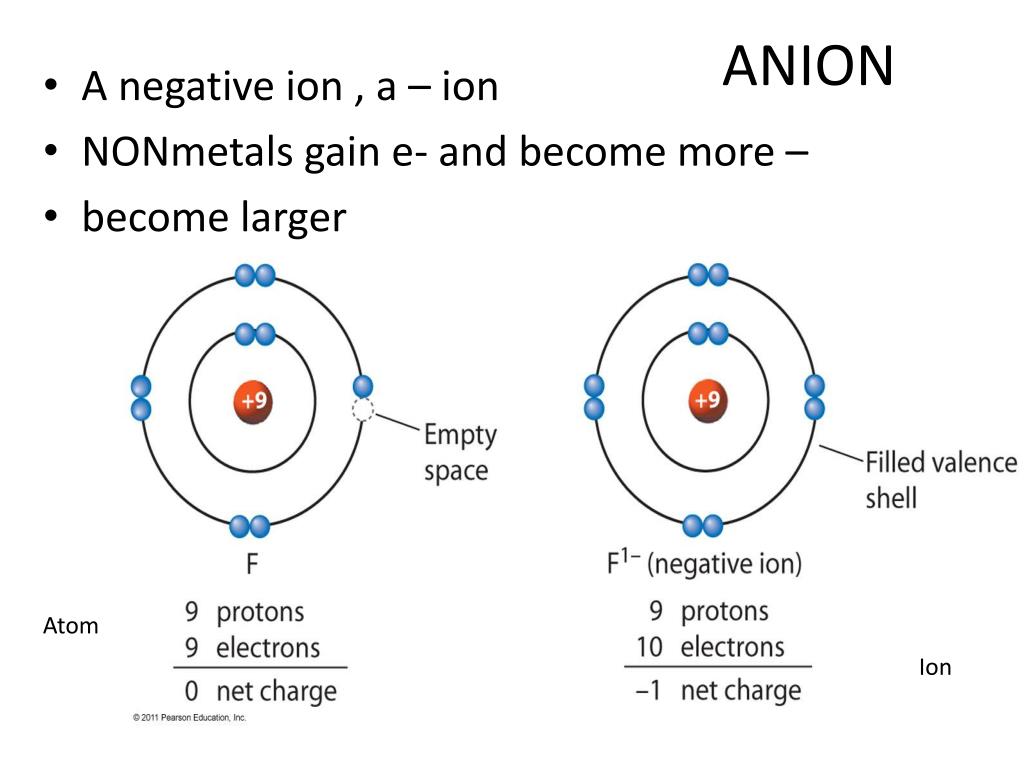
Atomic size trend anion series#
An isoelectronic series is useful in understanding the effects of gained or loss electrons on atom size.

For instance, lattices with O h and T d symmetries are considered to have high symmetry thus the electron densities of the component ions occupy relatively-spherical regions and ionic radii can be measured fairly accurately. The point group symmetry of a lattice determines whether or not the ionic radii in that lattice can be accurately measured (Johnson 1973). For a given ion, the ionic radius increases with increasing coordination number and is larger in a high-spin state than in a low-spin state.Īccording to group theory, the idea of ionic radii as a measurement of spherical shapes only applies to ions that form highly-symmetric crystal lattices like Na + and Cl. Ionic radius is not a permanent trait of an ion, but changes depending on coordination number, spin state, and other variables (Shannon 1976). After comparing many compounds, chemist Linus Pauling assign a radius of 140 pm to O 2- and use this as a reference point to determine the sizes of other Ionic Radii (Jensen 2010). However, it is to consistently and accurately determine the proportions of the ionic bonds. The ionic radius of an atom is measured by calculating its spatial proportions in an ionic bond with another ion within a crystal lattice. Measurement and Factors Affecting Ionic Radii


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
